Periodogram (FPScript)
Computes the segmented-overlapped Fourier spectrum.
Syntax
Periodogram(Signal, [ SpectrumType = SPECTRUM_DBNORM ], [ Window = WIN_HANNING+WIN_NORMALIZEAMPLITUDE ], [ Adjustment ], [ SegmentLength = 0 ], [ OverlapOrGap = 50 ], [ FFTLength = 0 ] [ , Peaks ])
The syntax of the Periodogram function consists of the following parts:
Part |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Signal |
The data to be analyzed. The data must have a constant sampling rate and must not contain void values. Permitted data structures are data series, data matrix, signal und signal series. All real data types are permitted. Void values are not permitted in this argument. For the X component additional restrictions do apply.The values must have a constant positive spacing. Void values are not permitted in this argument. If the argument is a list, then the function is executed for each element of the list and the result is also a list. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SpectrumType |
The spectral format to be computed. The argument SpectrumType can have the following values:
Permitted data structures are scalar value. All integral data types are permitted. If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. If this argument is omitted, it will be set to the default value SPECTRUM_DBNORM. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Window |
The fixed or adjustable data window to be applied to the data. The argument Window can have the following values:
Permitted data structures are scalar value. All integral data types are permitted. If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. If this argument is omitted, it will be set to the default value WIN_HANNING+WIN_NORMALIZEAMPLITUDE. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Adjustment |
The one-sided Fourier width as a multiple of the frequency interval. The valid range is window specific within 1.0 to 6.0. The default is 1.5 for a tapered cosine window and 3.0 for all other adjustable data windows. Permitted data structures are scalar value. All real data types are permitted. If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SegmentLength |
The length of individual data segments. The valid range is between 2 and the data length / 2. The default value 0 sets the segment length to the data length / 4. Permitted data structures are scalar value. All integral data types are permitted. If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. If this argument is omitted, it will be set to the default value 0. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
OverlapOrGap |
If this argument is specified as a positive number, then it specifies the percentage overlap of the data segments. If it is specified as a negative number, then its amount specifies the gap between each data segment in sample points. Permitted data structures are scalar value. All real data types are permitted. The value must be less or equal to 95. If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. If this argument is omitted, it will be set to the default value 50. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FFTLength |
The length of the Fourier transform. Zero padding applies if the FFT length is greater than the segment length. The valid range is from the segment length to the maximum limit of FFT. The default value is 0, which sets the FFT length equal to the segment length. Permitted data structures are scalar value. All integral data types are permitted. The value must be greater or equal to 0 and less or equal to 2147483648. If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. If this argument is omitted, it will be set to the default value 0. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Peaks |
If specified, then only band-interpolated peaks of the spectrum are output. The peaks can be specified as a number of peaks or determined using a dB threshold. Specify a number as a positive number from 1 to 100 without a unit. You can specify a dB threshold as a quantity with the unit dB between 0.01 dB and 300 dB, or as a negative number between -0.01 and -300 without a unit. Permitted data structures are scalar value. All real data types are permitted. If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. |
Remarks
The result has the data structure signal or signal series. If the argument Signal is a data series or data matrix, then the X-component of the result contains the Nyquist-normalized frequencies.
The following graph visualizes the settings for segment length, overlap, and FFT length:
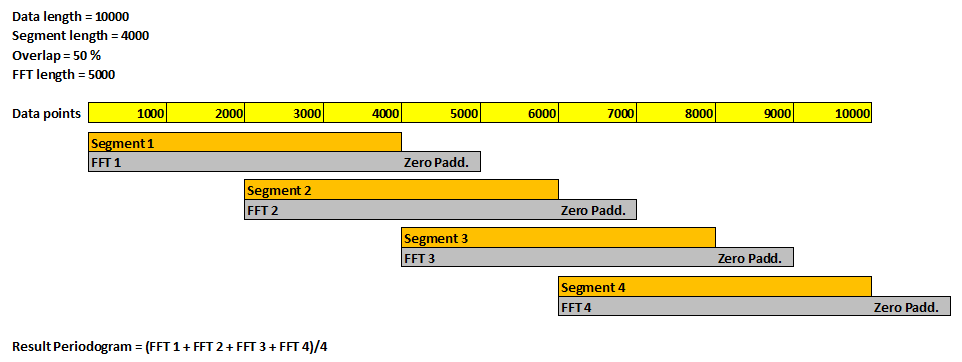
Available in
FlexPro Basic, Professional, Developer Suite
Examples
Periodogram(Signal, SPECTRUM_DBNORM, WIN_CHEBYSHEV, 4, 0, 90, 4096)
Calculates the periodogram for the equidistant signal 'Signal'. This method is used when a spectral estimation with low variance is required, such as for measuring power. dB is normalized as the spectrum type and the Chebyshev window type with the window adjustment of 4 is selected. The FFT length is 4096. This is an example from the Fourier Spectral Analysis Tutorial.
See Also
You might be interested in these articles
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from Facebook. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Instagram. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from X. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information