Distribution (FPScript)
Calculates various distribution or density functions.
Syntax
Distribution(X, Distribution, Parameter1 [ , Parameter2 ])
The syntax of the Distribution function consists of the following parts:
Part |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
X |
Contains the X values, i. e. the values of the random variable for which the distribution function or density function is to be calculated. When calculating a discrete distribution, the X values must be integral and positive. Permitted data structures are scalar value, data series und data matrix. All numeric data types are permitted. For complex data types the absolute value is formed. If the argument is a list, then the function is executed for each element of the list and the result is also a list. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution |
Specifies which distribution is to be calculated and whether the distribution function or density function is to be calculated. The argument Distribution can have the following values:
If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Parameter1 |
Specifies the first parameter for the distribution to be calculated. Permitted data structures are scalar value. All numeric data types are permitted. If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Parameter2 |
If necessary, specifies the second parameter of the distribution to be calculated. Permitted data structures are scalar value. All numeric data types are permitted. If the argument is a list, then the first element in the list is taken. If this is also a list, then the process is repeated. |
Remarks
The result always has the data type 64-bit floating point.
The distributions are calculated based on various approximation formulas. Before you use the distributions calculated with this function for statistical purposes, you should check whether the accuracy is sufficient for your task.
Available in
Option Enhanced Statistics
Examples
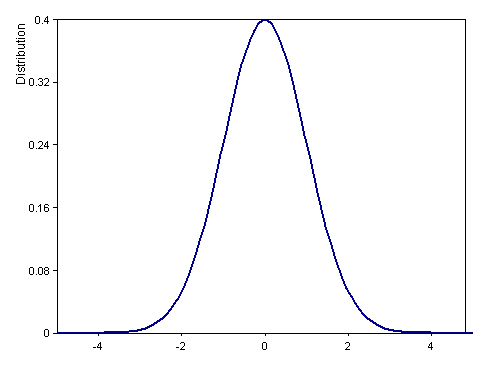
Dim x = (100, -5, 0.101010101010101)
Signal(Distribution(x, DISTRIBUTION_NORMAL + DISTRIBUTION_DENSITY, 0, 1), x)
Calculates the density function of the standard normal distribution (mean 0, variance 1) in interval [-5, 5].
See Also
References
[1] "Hartung, Joachim": "Statistik (Statistics), 9th Edition". "Oldenbourg Verlag GmbH, Munich",1993.ISBN 3-486-22055-1.
You might be interested in these articles
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from Facebook. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Instagram. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from X. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information